Childhood Trauma

9 Minutes
CONTENTS
Experts commonly term children as highly resilient as they can easily bounce back from just about any situation. However, specific traumatic experiences in childhood can lead to severe and potentially long-lasting effects that stretch into adulthood if left unresolved. Known as childhood trauma, the phenomenon is real and can result from anything that triggers feelings of helplessness in a child while disrupting their sense of security and safety. Be it physical, verbal, or sexual abuse, bullying in school, or a serious illness, multiple factors contribute to the development of childhood trauma. Fortunately, help is available for people who wish to move past their traumatic memories and restart a happy life.
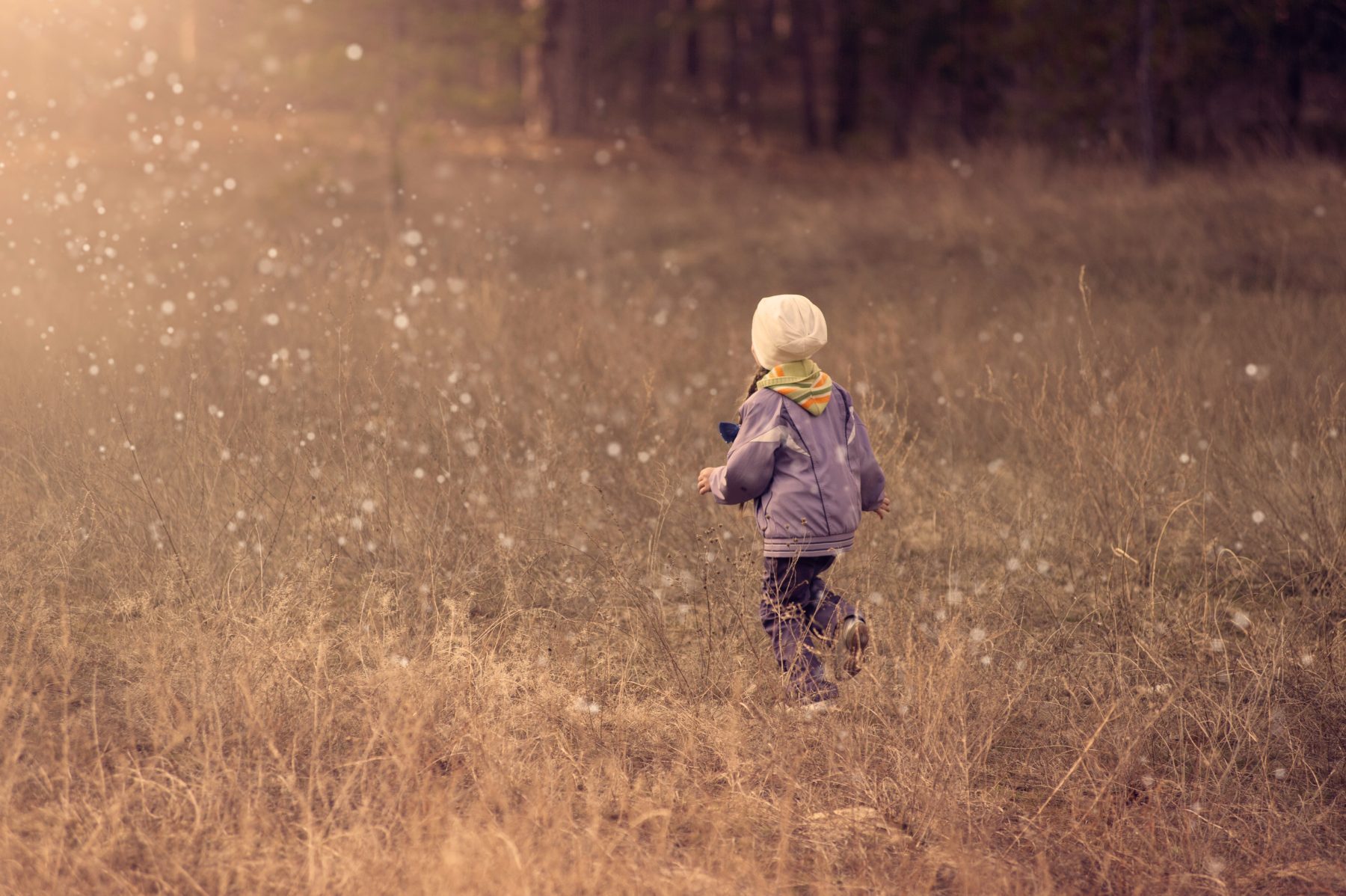

Childhood trauma refers to the painful memories triggered by any situation in which a child perceives themselves as in a dangerous, frightening, or overwhelming position. Traumatic events can make children scared and helpless in a way that goes far beyond their emotional and mental processing. These situations can either occur in the form of one-off events, like injuries or natural disasters, or continue to occur from repeated incidences of sexual, verbal, and physical abuse. All these events bring on the symptoms of psychological and emotional trauma in children that continue to haunt them well into their adult lives.
Childhood trauma can look different for different people; however, some core events seem to trigger it the most. Depending on these events, the following types of childhood trauma are most important to remember:
Physical abuse
As one of the most common examples of childhood trauma, physical abuse occurs when someone, usually an authoritative figure like a parent or teacher, uses their authority to injure you physically. Injuries may include cuts, scratches, bruises, broken bones, and burns.
Physical neglect
This type of childhood trauma stems from a failure of the caregiver to give you the physical resources you need to survive, such as clothing and food.
Emotional abuse
While many do not consider emotional manipulation abuse, the truth is they are a common trigger of childhood trauma. When someone intentionally tries to injure your dignity or emotional integrity, it easily falls into abuse. Emotional abuse can occur in the form of shaming, threatening, and scapegoating.
Sexual abuse
As one of the most common and equally damaging types of abuse, sexual abuse continues to affect millions of young boys and girls worldwide. This involves sexual exploitation, usually by a close family member or friend, which can lead to the destruction of their emotional stability, loss of confidence, and poor self-esteem, the effects of which continue to linger into adult life.
Loss of a caregiver
Losing a caregiver or parent can be devastating for any child. Even though a child may hardly be old enough to remember it, this type of bereavement can have far-reaching effects.
Emotional neglect
Emotional neglect is difficult to spot and the hardest to realize and move past as adults. If your caregiver has failed to form a nurturing connection with you, it comes under emotional neglect.
Natural disasters
Living through natural disasters can be painful for anyone, but such incidences can particularly affect young, developing children. Hurricanes, floods, and fires can induce trauma in different and unexpected ways, the effects of which can continue to affect children even if they reach adulthood.
Fortunately, experiencing a painful event does not always lead to the development of childhood trauma. Multiple factors contribute to its symptoms, including a child’s history of trauma and the protective factors available to them. Some of these factors are explained below:
The severity of the event
This includes:
- How serious was a perpetuating event?
- How bad was the child or someone they loved hurt?
- Were there police involved
- Was the child separated from their parents or caregivers?
- Did a family member or friend die
- Did the child undergo an interview by a police officer, counselor, or principal?
Proximity to the event
The following questions assess a child’s proximity to an event:
- Was the child a witness to the traumatic event?
- Did they experience it themselves or see it happening to someone else?
- Did they watch the event on television?
- Did they hear of the event from a loved one?
Caregivers’ reactions
This includes the following questions:
- Did the child’s caregiver believe that they were telling the truth?
- Did they take their concern seriously?
- How did the caregivers respond to the child, and how did they cope with the traumatic event themselves?
Prior history of trauma
- Has the child been exposed to any traumatic events in the past?
- If yes, how many and what was the intensity or severity of those events, and how did the child cope with them?
Family and community factors
- Was the child’s family supportive of their trauma-related struggles?
- Was the child under any cultural pressure to hide their traumatic experiences or feelings related to them?
Different people can have different responses to childhood trauma. Some of the most common responses include:
Passive-aggressive behavior
Adult survivors of childhood trauma typically deal with anger issues they do not know how to manage. Instead of confronting their painful emotions honestly, such people tend to bury them and resort to passive-aggressive behavior that forces them to isolate and destroy all-important relationships with others. Such people commonly strike out with sarcasm and later call it a mistake or joke. They are not comfortable enough to show their anger as they cannot estimate the consequences of doing it. So they try acting out passive-aggressively instead to protect themselves in a self-defeating way.
Attachment disorders
Children who acquire childhood trauma between the age of six months to three years are particularly vulnerable to difficulties forming healthy attachments with others. Referred to as reactive attachment disorder, it can affect their ability to establish adequate social relationships.
Lowered cognitive ability
When children regularly experience neglect or abuse, they often end up developing cognitive problems. These include memory, concentration problems, and poor verbal skills.
Altered states of consciousness
If childhood trauma continues to happen over the years, it may force children to enter a dissociative state. Since children cannot recognize different states of consciousness, they cannot stop themselves from slipping into them. These altered states force them to lose touch with their authentic selves and feel distant from things that bring value to their lives. Even after many years, such people continue relying on these delusional states to survive tough times.
Poor behavioral control
Many people with a history of childhood trauma become impulsive adults. Such people have a hard time controlling their behavior and do whatever they feel like as they have never learned to do otherwise. Some people adopt these behaviors as a way to gain the attention they never received in their childhood.
It is certainly not easy to face the pain experienced due to childhood trauma, but doing so is necessary to initiate recovery and healing. Someone who has been avoiding their pain and memories frequently experiences flashbacks or nightmares due to unresolved trauma. They may even experience panic attacks or develop depression as they cannot let go of the traumatic events they experienced as a child. Irrespective of the age at which you acquired these traumatic experiences, they can have a lasting impact on you.
Treatment for childhood trauma becomes critical if its associated memories start interfering with your daily functioning. You may notice experiencing unwanted emotional responses, such as frequently lashing out at your loved ones without knowing why. As you dig deeper, you will discover that your childhood wounds still continue to affect you and recognize that you are only rehashing your psychological trauma as an adult.
Unfortunately, the emotional trauma in childhood and the wounds related to it will not begin to heal unless you start openly addressing them. You likely feel guilt or shame because of what happened to you in the past, but remind yourself that these feelings are completely natural. However, they are not in any way going to help you move past the traumatic event. If anything, this shame and guilt only make people rely on unhealthy coping methods, such as substance abuse.
For effectively healing from the wounds you acquired in childhood, it is important to face your past and manage the stress they are causing. Remember that you do not have to go through the recovery process alone, as plenty of resources are available to help. One of the best ways to start addressing childhood trauma is by seeking therapy. Working with a trauma specialist who appreciates the essence of positive psychology can be extremely helpful. Whether online or in person, therapists can help counsel you and support you toward healing. They typically rely on trauma-informed care to handle child neglect and abuse victims. As soon as you connect with a therapist, they will most likely conduct a trauma assessment to confirm the extent and severity of your underlying issue and screen you for other psychiatric illnesses, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Depending on these screening results, they may discuss different therapy options, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which exclusively focuses on healing by helping victims recognize and eradicate all damaging behaviors stemming from childhood trauma.
Check out our luxury rehab facilities.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of childhood trauma?
The following are the common symptoms suggestive of childhood trauma:
Low mood
Anxiety
Dissociation
Racing heart
Feelings of denial, shock, or confusion
Anger issues
Sleep problems
Muscle tension
Lack of focus
Unexplained aches and pains
Lack of energy or fatigue
How to deal with childhood trauma at home?
Treatment for childhood trauma depends on the duration and severity of symptoms. Most people with this issue require professional attention and treatment to cope better with everyday life. However, there are certain things you can do at home to increase the chances of recovery. These include:
Avoiding drugs and alcohol
Exercising regularly
Maintaining a consistent sleeping and eating schedule
Spending more time with people who love and support you
How can I help my child cope with early childhood trauma?
If recognized early on, there are many things you can do as a parent to resolve early childhood trauma in a child. Some of these tips include the following:
Encourage the child to discuss their feelings and constantly validate their emotions
Answer their questions as honestly as possible
Make them understand that it is not their fault
Make a daily routine and stick to it as much as possible
Reassure your child that you will do anything you can to keep them safe
Practice patience and allow your child to recover at their own pace. Do not rush things
HOW THE BALANCE CAN HELP
The Balance RehabClinic is a leading provider of luxury addiction and mental health treatment for affluent individuals and their families, offering a blend of innovative science and holistic methods with unparalleled individualised care.
A UNIQUE METHOD
a successful and proven concept focusing on underlying causesOur program consists of treating only one client at a time individually designed to help you with all the problematic aspects of your life. All individual treatment sessions will be held at your private residence.
more infoYour program is designed based on your personal needs. The team will exchange daily information and adjust the schedule as we go. Our therapists will work with you treating the root causes and not just the symptoms and goes beyong your stay to ensure lasting success.
more infoOur biochemical imbalance can be affected by diet and stressful life events, but it often goes back to genetics and epigenetics. We do specific biochemical laboratory testing to determine an individual’s biochemical imbalance. Combining the results of the lab tests with anamnestic information and clinical tests, we prescribe an individualized and compounded vitamin, mineral, nutrient protocol to help recover from various disease states.
more infoOur experts combine the best from psychological treatment, holistic medicine to support you individually and providing complementary therapies all coordinated from one source working complementing each other integrative.
more infoUsing latest cutting-edge technology-based therapies such as Neurofeedback, tDCS, and SSP, we can track the biological patterns of your body, giving us valuable insight into your health and well-being as well support your brain and body performance and recovery with neuromodulation.
more infoComplex trauma is often a key factor to distress mental and physical state. The Balance provides a safe space along integrated trauma treatment methods to enable healing.
more infoLASTING APPROACH
0 Before
Send Admission Request
0 Before
Define Treatment Goals
1 week
Assessments & Detox
1-4 week
Psychological & Holistic Therapy
4 week
Family Therapy
5-8 week
Aftercare
12+ week
Refresher Visit
Trauma & PTSD Insights
latest news & research on Trauma & PTSD
Trauma And Epigenetics
Traumatic experiences can lead to long-lasting epigenetic changes, potentially contributing to mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
read moreBest Trauma Treatment Centers
Joining an intensive trauma treatment center is essential because these specialized facilities offer a comprehensive approach to recovery
read moreBest PTSD Treatment Centers
Many PTSD centers offer alternative and complementary therapies to support traditional treatments.
read moreChildhood Emotional Neglect
Childhood emotional neglect is a pervasive issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide.
read more